My on going project
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are opportunistic pathogens found in soil and water sources such as shower heads, faucets, and plumbing systems. Infections have been increasing worldwide, with particularly sharp rises in the United States (Spaulding et al., 2017).
However, current therapies remain inadequate due to intrinsic antibiotic resistance and prolonged treatment requirements, underscoring the urgent need for novel therapeutics and deeper insight into NTM physiology under stress conditions.
Cyclic dipeptides (CDPs) as novel antimicrobials – I am investigating the antimicrobial activity of CDPs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and M. abscessus (bolletii 103). This includes characterizing their mechanism of action, evaluating cytotoxicity in THP-1–derived macrophages, and assessing synergistic interactions with clinically used antibiotics.
Development of environmental reservoir models – To better understand NTM persistence outside the host, I am testing M. abscessus survival under PBS starvation and tap water exposure. These simplified models mimic environmental reservoirs and provide insight into adaptation strategies that may contribute to infection risk.
Defining metabolic shifts in M. abscessus under stress – Using LC/MS-based metabolomics, I am analyzing metabolic and lipidomic shifts induced by CDP treatment, PBS starvation, and tap water exposure compared to replicating conditions. This work aims to identify vulnerable pathways that may serve as potential antibiotic targets.
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria(NTM)
NTM do not include M. tuberculosis (the cause of tuberculosis) or M. leprae (the cause of Hansen's disease).
More than 190 recognized species (types) of NTM
About five of the NTM species cause disease in Human
(MAC; Mycobacterium Avium Complex, M. abscessus, M. kansasii, M. xenopi, and M. malmoense)
Global NTM Infection or Diseases Trends
(Dahl et al., 2022)
NTM infection: Detection of NTM in a clinical specimen (e.g., sputum)
NTM disease : Clinical illness caused by NTM, confirmed by symptoms + lab + imaging
Epidemiological trends of pulmonary NTM disease and tuberculosis (1971 - 2014)
While TB incidence has steadily declined over the decades, the incidence of NTM pulmonary disease has been rising.
Even as we gain control over tuberculosis, nontuberculous mycobacteria are becoming an emerging threat, and are much harder to treat with current drug regimens.
That’s why understanding the biology and survival mechanisms of pathogens like M. abscessus is now more important than ever.
Total: 3,104 patients (Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex ;MTBC 87.3%, Nontuberculous Mycobacteria ;NTM 12.7%)
MTBC steadily declined (386 → 241)
NTM stable, peak in 2018 (n = 57)
Proportion of NTM shows slight upward trend
Trends in MTBC and NTM Cases (2013–2022)
Przybylski et al., Pathogens, 2023
One of the NTM species
Found in soil and water (environmental bacterium)
An opportunistic pathogen.
Causes serious chronic lung disease in individuals with underlying conditions
Mycobacterium abscessus ?
Infects people with chronic lung conditions:
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Bronchiectasis
Epidemiological Trends of M. abscessus (MABS)
Increasing globally and are particularly prevalent in Southeast Asia and Latin America.
MABS is the second most prevalent species, accounting for 15–20% of pulmonary NTM cases in US.
In South Korea and Japan, MABS is the second most common cause of NTM disease, responsible for 20–30% of infections (Shin et al., 2013; Umrao et al., 2016).
Cyclic dipeptides (CDPs) as novel antimicrobials
What Are Cyclic Dipeptides (CDPs)?
Mixture received from collaborators
Initial compound derived from lactobacillus
Observed antimicrobial effects on other bacteria
CDP cytotoxicity Test on THP-1 Macrophages by CyQUANT Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
Figure 2 : Cytotoxicity assay in THP-1-derived marophages
Following the identification of CDPs’ activity against M. abscessus, I assessed their cytotoxicity in THP-1–derived macrophages and confirmed the absence of toxic effects
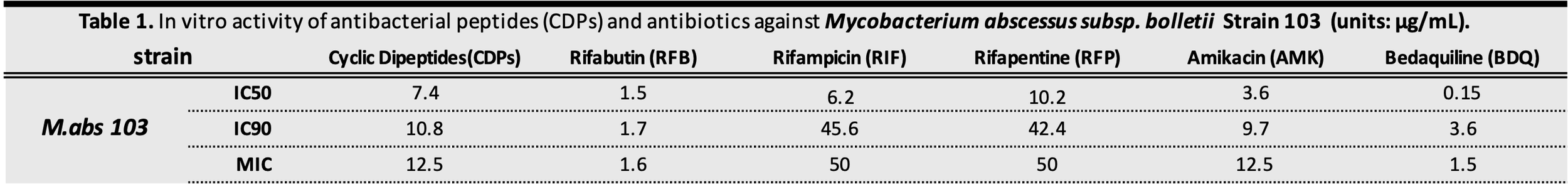
Antibiotics and antibacterial peptides CDPs MIC and IC50 on M.abs
To characterize M. abscessus strain 103 that I am studying, I determined the MIC and IC50 values of several antibiotics and antibacterial peptides (CDPs) to evaluate their comparative in vitro activities.
2. Development of environmental reservoir models
Figure 3: M. abscessus CFU counts under PBS + Tween80(0.025%) or Tap water + Tween80(0.025%)
Tap water was tested as an environmental reservoir condition, and PBS as a nutrient starvation condition.
I compared survival and growth of M. abscessus under these two stresses relative to replicating cell.
Compared to PBS(nutrient starvation environment), Tap water ( environmental model)
CDPs Activity under Different Conditions (Regular vs PBS vs Tap water)
Figure 4. Increased susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus to CDPs under PBS starvation and Tap water exposure compared to regular medium.
Compared to regular medium, M. abscessus became more susceptible to CDPs under PBS, and even more sensitive under Tap water, indicating enhanced vulnerability in environmental or starvation conditions.